Petroleum
Petrodollar recycling
Petrodollar recycling is the international spending or investment of a country's revenues from petroleum exports ("petrodollars").[3] It generally refers to the phenomenon of major petroleum-exporting nations, mainly the OPEC members plus Russia and Norway, earning more money from the export of crude oil than they could efficiently invest in their own economies.[4] The resulting global interdependencies and financial flows, from oil producers back to oil consumers, can reach a scale of hundreds of billions of US dollars per year – including a wide range of transactions in a variety of currencies, some pegged to the US dollar and some not. These flows are heavily influenced by government-level decisions regarding international investment and aid, with important consequences for both global finance and petroleum politics.[5] The phenomenon is most pronounced during periods when the price of oil is historically high.[6]
The term petrodollar was coined in the early 1970s during the oil crisis, and the first major petrodollar surge (1974–1981) resulted in more financial complications than the second (2005–2014).[7]
In August 2018, Venezuela declared that it would price its oil in Euros, Yuan and other currencies.[8][9]
Capital flows
Background
Especially during the years 1974–1981 and 2005–2014, oil exporters amassed large surpluses of "petrodollars" from historically expensive oil.[1][2][10] (The word has been credited alternately to Egyptian-American economist Ibrahim Oweiss and to former US Secretary of Commerce Peter G. Peterson, both in 1973.)[11][12][13] These petrodollar surpluses could be described as net US dollar-equivalents earned from the export of petroleum, in excess of the internal development needs of the exporting nations.[14] The surpluses could not be efficiently invested in their own economies, due to small populations or being at early stages of industrialization; but the surpluses could be usefully invested in other nations, or spent on imports such as consumer products, construction supplies, and military equipment. Alternatively, global economic growth would have suffered if that money was withdrawn from the world economy, while the oil-exporting nations needed to be able to invest profitably to raise their long-term standards of living.[15]
1974–1981 surge
While petrodollar recycling reduced the short-term recessionary impact of the 1973 oil crisis, it caused problems especially for oil-importing countries that were paying much higher prices for oil, and incurring long-term debts. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimated that the foreign debts of 100 oil-importing developing countries increased by 150% between 1973 and 1977, complicated further by a worldwide shift to floating exchange rates. Johan Witteveen, the Managing Director of the IMF, said in 1974: "The international monetary system is facing its most difficult period since the 1930s."[16] The IMF administered a new lending program during 1974–1976 called the Oil Facility. Funded by oil-exporting nations and other lenders, it was available to nations suffering from acute problems with their balance of trade due to the rise in oil prices, notably including Italy and the UK as well as dozens of developing countries.[17]
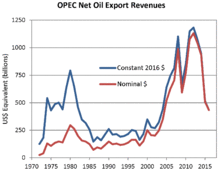
From 1974 through 1981, the total current account surplus for all members of OPEC amounted to US$450 billion, without scaling-up for the subsequent decades of inflation. Ninety percent of this surplus was accumulated by the Arab countries of the Persian Gulf and Libya, with Iran also accumulating significant oil surpluses through 1978 before suffering the hardships of revolution, war and sanctions.[14]
Large volumes of Arab petrodollars were invested directly in US Treasury securities and in other financial markets of the major industrial economies, often directed discreetly by government entities now known as sovereign wealth funds.[18][19] Many billions of petrodollars were also invested through the major commercial banks of the US and Europe. In fact, the process contributed to the growth of the Eurodollar market as a less-regulated rival to US monetary markets. As the recessionary condition of the world economy made investment in corporations less attractive, bankers and well-financed governments lent much of the money directly to the governments of developing countries, especially in Latin America such as Brazil and Argentina[14] as well as other major developing nations like Turkey. The 1973 oil crisis had created a vast dollar shortage in these countries; however, they still needed to finance their imports of oil and machinery. In early 1977, when Turkey stopped heating its prime minister's office, opposition leader Suleyman Demirel famously described the shortage as: "Turkey is in need of 70 cents."[20] As political journalist William Greider summarized the situation: "Banks collected the deposits of revenue-rich OPEC governments and lent the money to developing nations so they could avoid bankruptcy."[21] In subsequent decades, many of these developing nations found their accumulated debts to be unpayably large, concluding that it was a form of neocolonialism from which debt relief was the only escape.[22]
2005–2014 surge
In the 2005–2014 petrodollar surge, financial decision-makers were able to benefit somewhat from the lessons and experiences of the previous cycle. Developing economies generally stayed better balanced than they did in the 1970s; the world economy was less oil-intensive; and global inflation and interest rates were much better contained. Oil exporters opted to make most of their investments directly into a diverse array of global markets, and the recycling process was less dependent on intermediary channels such as international banks and the IMF.[24][25][26]
Thanks to the historic oil price increases of 2003–2008, OPEC revenues approximated an unprecedented US$1 trillion per year in 2008 and 2011–2014.[2] Beyond the OPEC countries, substantial surpluses also accrued to Russia and Norway,[10] and sovereign wealth funds worldwide amassed US$7 trillion by 2014–2015.[27] Some oil exporters were unable to reap the full benefits, as the national economies of Iran, Iraq, Libya, Nigeria and Venezuela all suffered from multi-year political obstacles associated with what economists call the "resource curse".[28][29] Most of the other large exporters accumulated enough financial reserves to cushion the shock when oil prices and petrodollar surpluses fell sharply again from an oil supply glut in 2014–2017.[30]
Foreign aid
Oil-exporting countries have used part of their petrodollar surpluses to fund foreign aid programs, as a prominent example of so-called "checkbook diplomacy" or "petro-Islam". The Kuwait Fund was an early leader since 1961, and certain Arab nations became some of the largest donors in the years since 1974, including through the IMF and the OPEC Fund for International Development.[14][31][32] Oil exporters have also aided poorer nations indirectly through the personal remittances sent home by tens of millions of foreign workers in the Middle East,[33] although their working conditions are generally harsh.[34] Even more controversially, several oil exporters have been major financial supporters of armed groups challenging the governments of other countries.[35][36][37][38]
High-priced oil allowed the USSR to support the struggling economies of the Soviet bloc during the 1974–1981 petrodollar surge, and the loss of income during the 1980s oil glut contributed to the bloc's collapse in 1989.[39] During the 2005–2014 petrodollar surge, OPEC member Venezuela played a similar role supporting Cuba and other regional allies,[40] before the 2014–2017 oil downturn brought Venezuela to its own economic crisis.[41]
Petrodollar warfare
The term petrodollar warfare refers to the motivation of US military offensives being to preserve by force the status of the United States dollar as the world's dominant reserve currency and as the currency in which oil is priced. The term was coined by William R. Clark, who has written a book with the same title. The phrase oil currency war is sometimes used with the same meaning.
The hypothesis
The United States dollar remains de facto world currency.[42] Accordingly, almost all oil sales throughout the world are denominated in United States dollars (USD).[43] Because most countries rely on oil imports, they are forced to maintain large stockpiles of dollars in order to continue imports. This creates a consistent demand for USDs and ostensibly supports the USD's value, regardless of economic conditions in the United States.
According to proponents of the petrodollar warfare hypothesis, this in turn allegedly allows the US government to gain revenues through seignorage and by issuing bonds at lower interest rates than supposedly they otherwise would be able to. As a result, the U.S. government, according to this theory, can run higher budget deficits at a more sustainable level than most other countries can. The theory points out that a stronger USD also means that goods imported into the United States are relatively cheap (although the country's exports become relatively more expensive for the rest of the world).
Another component of the hypothesis is that the price of petroleum is more stable in the U.S. than anywhere else since importers do not need to worry about exchange rate fluctuations. Since the U.S. imports a great deal of oil, its markets are heavily reliant on oil and its derivative products (jet fuel, diesel fuel, gasoline, etc.) for their energy needs. As the price of oil can be an important political factor, U.S. administrations are quite sensitive to the price of oil.
Political competitors of the United States therefore have some interest in seeing oil denominated in euros or other currencies. The EU could also theoretically accrue the same benefits if the euro replaced the dollar.
History
The petrodollar system originated in the early 1970s in the wake of the Bretton Woods collapse. President Richard Nixon and his Secretary of State, Henry Kissinger, feared that the abandonment of the international gold standard under the Bretton Woods arrangement (combined with a growing US trade deficit, and massive debt associated with the ongoing Vietnam War) would cause a decline in the relative global demand of the U.S. dollar.[44] In a series of meetings, the United States — represented by then U.S. Secretary of State Henry Kissinger — and the Saudi royal family made an agreement. The United States would offer military protection for Saudi Arabia's oil fields, and in return the Saudis would price their oil sales exclusively in United States dollars (in other words, the Saudis were to refuse all other currencies, except the U.S. dollar, as payment for their oil exports).
By 1975, all of the oil-producing nations of OPEC had agreed to price their oil in dollars and to invest surplus oil proceeds in U.S. government debt securities in exchange for similar offers by the U.S.[45]
Political events

In 2000, Iraq converted all its oil transactions under the Oil for Food program to euros,[46] even though the move was deemed by analysts to "fly in the face of financial logic",[46] since it meant that Iraq would earn less interest on its oil revenues, which were held in a UN-monitored escrow account in New York. Also, the switch would create "cumbersome new administrative processes" because Baghdad decided to keep also its existing deposits in dollars, which meant that the oil-for-food program would maintain two accounts, one in dollars and one in euros.[46]
Several commentators writing contemporaneously with the buildup to the invasion[47][48][49] linked Iraq's Nov 2000 re-denomination of oil from USD to euros and the possibility of more widespread adoption of the euro as an oil pricing standard to the risk that that would place on the post-Bretton Woods use of the USD as the international reserve currency and the impact that that would have on the US economy, and theorised that one of the fundamental purposes for war in Iraq would be to force Iraq to revert to pricing its oil in USD.
After the U.S. invaded Iraq in 2003, Iraq returned the denomination of its oil sales to the US dollar, despite the greenback's then-fall in value.[50]
The Government of the Islamic Republic of Iran ostensibly takes this theory as fact. As retaliation to this policy, which is seen by Tehran as "neoimperialism",[51] Iran made an effort to create its own bourse, which started selling oil in gold, euros, dollars, and Japanese yen.[52] In mid-2006 Venezuela indicated "support" of Iran's decision to offer global oil trade in the euro currency.[53] Muammar Gaddafi of Libya had tried to implement the gold-for-oil plan in 2011[54] and the introduction of a Libyan gold dinar.
In 2005, William Roberts Clark, Professor and Faculty Associate, Political Science Department, Center for Political Studies, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, published a work which claimed that a "petrodollar warfare" was under way between mainly the euro and the United States dollar waged in the field of world petroleum trade.[55]
Over the years, multiple scholars expressed the view that the Iraq War was conducted to re-assert the dollar hegemony in the wake of Saddam Hussein's attempts to switch from petrodollar in the oil trade and to sell Iraqi oil in exchange for other currencies or commodities.[56][57][58]
Gallery of notable examples
These images illustrate the diversity of major petrodollar recycling activities, in roughly chronological order:
See also
References
- ^ a b "OPEC Revenues Fact Sheet". U.S. Energy Information Administration. January 10, 2006. Archived from the original on January 7, 2008.
- ^ a b c "OPEC Revenues Fact Sheet". U.S. Energy Information Administration. May 15, 2017. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
- ^ Myers, Amy; Elass, Jareer. "War and the Oil Price Cycle". Jpurnal of International Affairs. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ Hertzberg, Hendrik (May 2, 2004). "In the soup - Bob Woodward's plan of attack". New Yorker. Retrieved April 10,2019.
- ^ Coll, Steve (August 10, 2014). "Oil and erbil". New Yorker. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ Nsouli, Saleh M. (March 23, 2006). "Petrodollar Recycling and Global Imbalances". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved January 14, 2017.
- ^ Kinzer, Stephen (2008). All the Shah's Men: An American Coup and the Roots of Middle East Terror. Wiley. ISBN 978-0470185490.
- ^ "US dollars no longer a quote currency in Venezuela". Xinhua Net. October 18, 2018. Retrieved October 19, 2018.
- ^ "Fintech is the new oil in the Middle East and North Africa". Forbes. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ a b "Petrodollar Profusion". The Economist. April 28, 2012. Retrieved February 7, 2016.
- ^ "Personality: Ibrahim M. Oweiss". Washington Report on Middle East Affairs. December 26, 1983. p. 8. Retrieved January 11, 2017.
In March 1973... Two weeks after Dr. Oweiss had used the word – at an international monetary seminar held at Columbia University's Arden House in Harriman, New York – it was picked up by a prestigious economics commentator in The New York Times.
According to the Oweiss and NYT websites, it appears that these events actually occurred in March 1974. - ^ Rowen, Hobart (July 9, 1973). "Peterson Urges Cooperation". The Washington Post. p. A1. Retrieved February 5,2016.
He thinks the U.S. should give more study to ways in which the excess funds – he calls them petro dollars – can be soaked up.
- ^ Popik, Barry (February 1, 2012). "Petrodollar". Retrieved January 11, 2017.
Georgetown University economics professor Ibrahim Oweiss has written about petrodollars and is credited with the word's coinage by Wikipedia, but there is insufficient documentary evidence that he used the term first in 1973. Former commerce secretary Peter G. Peterson was credited with using 'petrodollar' in a July 1973 Washington Post article.
- ^ a b c d Oweiss, Ibrahim M. (1990). "Economics of Petrodollars". In Esfandiari, Haleh; Udovitch, A.L. (eds.). The Economic Dimensions of Middle Eastern History. Darwin Press. pp. 179–199. Retrieved January 31, 2016.
- ^ "Petrodollar Problem". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved January 31, 2016.
- ^ "Recycling Petrodollars". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved January 31, 2016.
- ^ Neu, Carl Richard (August 1977). "International Balance of Payments Financing and the Budget Process". U.S. Congressional Budget Office. pp. 27–29. Retrieved February 5, 2016.
- ^ Spiro, David E. (1999). The Hidden Hand of American Hegemony: Petrodollar Recycling and International Markets. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. pp. 74–75. ISBN 0-8014-2884-X. Retrieved February 8, 2016.
- ^ Wong, Andrea (May 30, 2016). "The Untold Story Behind Saudi Arabia's 41-Year U.S. Debt Secret". Bloomberg News. Retrieved May 31, 2016.
- ^ Özel, Işık (2014). State–Business Alliances and Economic Development: Turkey, Mexico and North Africa. Routledge. p. 34. ISBN 978-1-317-81782-6. Retrieved January 31, 2016.
- ^ Greider, William (1987). Secrets of the Temple. Simon & Schuster. p. 340. ISBN 978-0-671-47989-3. Retrieved January 31, 2016.
- ^ Carrasco, Enrique; McClellan, Charles; Ro, Jane (April 2007). "Foreign Debt: Forgiveness and Repudiation". The E-Book on International Finance & Development. University of Iowa. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved June 6, 2011.
- ^ "Federal Reserve Economic Data graph". Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. Retrieved August 25, 2016.
- ^ Lubin, David (March 19, 2007). "Petrodollars, emerging markets and vulnerability" (PDF). Citigroup. Retrieved January 31, 2016.
- ^ "Recycling the Petrodollars". The Economist. November 10, 2005. Retrieved February 14, 2016.
- ^ Oxford Analytica (August 11, 2008). "World Economy Less Vulnerable To Petrodollars". Retrieved January 13, 2017.
- ^ Bianchi, Stefania (February 22, 2016). "Sovereign Wealth Funds May Sell $404 Billion of Equities". Bloomberg News. Retrieved February 22, 2016.
- ^ "The Resource Curse" (PDF). Natural Resource Governance Institute. March 2015. Retrieved January 22, 2017.
- ^ Aguilera, Roberto F.; Radetzki, Marian (2015). The Price of Oil. Cambridge University Press. pp. 87–89. ISBN 978-1-31643242-6. Retrieved January 22, 2017.
- ^ Blas, Javier (April 13, 2015). "Oil-Rich Nations Are Selling Off Their Petrodollar Assets at Record Pace". Bloomberg News. Retrieved February 14, 2016.
- ^ "Timeline". Kuwait Fund. Retrieved January 22, 2017.
- ^ Hubbard, Ben (June 21, 2015). "Cables Released by WikiLeaks Reveal Saudis' Checkbook Diplomacy". The New York Times. Retrieved February 16, 2016.
- ^ Mukherjee, Andy (February 4, 2016). "Oil's Plunge Spills Over". Bloomberg News. Retrieved February 4, 2016.
- ^ Davis, Mike (September–October 2006). "Fear and Money in Dubai". New Left Review (41). Retrieved February 12,2016.
Dubai is capitalized just as much on cheap labour as it is on expensive oil, and the Maktoums, like their cousins in the other emirates, are exquisitely aware that they reign over a kingdom built on the backs of a South Asian workforce.
- ^ "Iranian General: Tehran Arming 'Liberation Armies'". Associated Press. October 27, 2008. Retrieved March 29,2017.
- ^ Weinberg, Leonard; Martin, Susanne (2016). The Role of Terrorism in 21st-Century Warfare. Oxford University Press. "Libya", pp. 207–208. ISBN 978-1-78499764-9. Retrieved March 29, 2017.
- ^ Cockburn, Patrick (October 14, 2016). "US allies Saudi Arabia and Qatar are funding ISIS". The Independent. Retrieved March 29, 2017.
- ^ Pacepa, Ion Mihai (August 24, 2006). "Russian Footprints". National Review. Archived from the original on January 9, 2015.
- ^ McMaken, Ryan (November 7, 2014). "The Economics Behind the Fall of the Berlin Wall". Mises Institute. Retrieved January 12, 2016.
High oil prices in the 1970s propped up the regime so well, that had it not been for Soviet oil sales, it's quite possible the regime would have collapsed a decade earlier.
- ^ Gibbs, Stephen (August 24, 2005). "Venezuela ends upbeat Cuba visit". BBC. Retrieved November 28, 2016.
- ^ Polanco, Anggy (July 17, 2016). "Venezuelan shoppers flock across border to Colombia". Reuters. Retrieved December 31, 2016.
- ^ Schulmeister, Stephan (March 2000). "Globalization without Global Money: The Double Role of the Dollar as National Currency and World Currency". Journal of Post Keynesian Economics. 22 (3): 365–395. doi:10.1080/01603477.2000.11490246. ISSN 0160-3477. S2CID 59022899.
- ^ "Ahmadinejad: Remove US dollar as major oil trading currency" Archived September 1, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, China Daily, 19 November 2007
- ^ Clark, William R. (2005). Petrodollar Warfare. Canada: New Society Publishers. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-86571-514-1.
- ^ Clark, William R. (2005). Petrodollar Warfare. Canada: New Society Publishers. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-86571-514-1.
- ^ a b c "Iraq: Baghdad Moves To Euro" by Charles Recknagel, Radio Free Europe website, 1 November 2000
- ^ "The Real Reasons for the Upcoming War With Iraq". Archived from the original on March 22, 2020. Retrieved March 9, 2020.
- ^ "Oil, Currency and the War in Iraq". Archived from the original on October 3, 2019. Retrieved March 9, 2020.
- ^ "It's not about oil or Iraq. It's about the US and Europe going head-to-head on world economic dominance". Archived from the original on December 23, 2017. Retrieved March 9, 2020.
- ^ "Iraq returns to international oil market" by Carola Hoyos and Kevin Morrison, Financial Times, June 5, 2003 (from TheDossier.com archive)
- ^ What the Iran 'nuclear issue' is really about by Chris Cook, Asia Times Online, January 21, 2006
- ^ Why Iran's oil bourse can't break the buck by F. William Engdahl, Asia Times Online, March 10, 2006
- ^ "Venezuela mulls euro oil switch". BBC News. December 22, 2006.
- ^ "Gaddafi gold-for-oil, dollar-doom plans behind Libya 'mission'?". www.thepeoplesvoice.org. Retrieved September 4,2018.
- ^ Petrodollar Warfare website of William R. Clark
- ^ Shipley, Tyler (March 2007). "Currency Wars: Oil, Iraq, and the Future of Us Hegemony". Studies in Political Economy. 79 (1): 7–34. doi:10.1080/19187033.2007.11675090. ISSN 0707-8552. S2CID 154178693.
- ^ Shor, Francis. "War in the era of declining US global hegemony." Journal of Critical Globalisation Studies 2 (2010): 65-81.
- ^ Gokay, Bulent. "The beginning of the end of the petrodollar: What connects Iraq to Iran." Alternatives: Turkish Journal of International Relations 4.4 (2005).
- ^ "Major Foreign Holders of Treasury Securities". U.S. Department of the Treasury. December 15, 2015. Archived from the original on January 3, 2016.
- ^ Taylor, Edward (September 18, 2014). "Kuwait Investment Authority says to expand Germany investments". Reuters. Retrieved January 17, 2017.
The KIA... is the largest shareholder in Daimler.
- ^ Al Saleh, Anas K. (September 18, 2014). "KIA/Daimler 40th Anniversary Celebrations" (PDF). Kuwait Investment Authority. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 18, 2017. Retrieved January 17, 2017.
From a 14.6% stake of around US$329 million acquisition in December 1974, the KIA is now the largest consistent shareholder in Daimler over 40 years where our 6.9% stake is currently valued around $7 billion.
- ^ Castor, Belmiro V.J. (2003). Brazil Is Not for Amateurs (English, 2nd ed.). Xlibris. p. 202. ISBN 978-1-46910432-4. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
International bankers... began to invest huge amounts of those petro-dollars in Brazil and other developing countries..., allowing them to finance gigantic infrastructure works like the Itaipu Hydroelectric Plant.
- ^ "Shah Faisal Mosque". Lonely Planet. Retrieved March 29, 2017.
Most of its cost (pegged at about US$120 million today) was a gift from King Faisal of Saudi Arabia.
- ^ Zubok, Vyadislav M. (2010). "Soviet foreign policy from détente to Gorbachev, 1975–1985". In Leffler, Melvyn P.; Westad, Odd Arne (eds.). The Cambridge History of the Cold War: Volume III, Endings. Cambridge University Press. pp. 109–110. ISBN 978-1-31602563-5. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
The former head of the Soviet planning agency, Nikolai Baibakov, recalled that 'what we got for oil and gas' was $15 billion in 1976–80 and $35 billion in 1981–85. Of this money, the Soviets spent, respectively, $14 billion and $26.3 billion to buy grain, both to feed the cattle on collective farms and to put bread on the tables of Soviet citizens.
- ^ Mohr, Charles (August 22, 1981). "Saudi AWACS Deal Passes $8 Billion". The New York Times. Retrieved November 5, 2016.
The price of the arms sale gives increased weight to an argument that in part it should be approved because it helps to 'recycle petrodollars'.
- ^ Feder, Barnaby J. (September 8, 1985). "Harrod's New Owner: Mohamed al-Fayed; A Quiet Acquisitor Is Caught in a Cross Fire". The New York Times. Retrieved January 16, 2017.
This was a dream come true for the family, which built its fortune... first in the oil-rich countries of the Persian Gulf.
- ^ "Mohammed Fayed sells Harrods store to Qatar Holdings". BBC. May 8, 2010. Retrieved February 7, 2016.
- ^ "Russian businessman buys Chelsea". BBC. July 2, 2003. Retrieved March 23, 2016.
- ^ Critchley, Mark (April 12, 2015). "Roman Abramovich reaches 700 games as Chelsea owner – but how does his reign stack up against the rest?". The Independent. Retrieved August 1, 2016.
Since the Russian oligarch began pouring petro-dollars into Stamford Bridge, he has turned one of English football's underachieving clubs into an established powerhouse.
- ^ Delaney, Miguel (February 2, 2014). "The colossal wealth of Manchester City and Chelsea is changing the landscape of British football". The Sunday Mirror. Retrieved August 1, 2016.
It should not escape notice that this is the first true title showdown, and first genuine title race, between the petrodollar clubs.
- ^ Corrales, Javier (December 2005). "The Logic of Extremism: How Chávez Gains by Giving Cuba So Much" (PDF). Inter-American Dialogue. Retrieved November 29, 2016.
In return for oil, Cuba is sending Venezuela between 30,000 and 50,000 technical staff. As many as 30,000 Cubans in Venezuela are presumably medical doctors.
- ^ Gaddy, James (January 5, 2017). "Emirates Has Invested $500 Million to Build a 'Fort Knox' of Wine". Bloomberg News. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
Since the Dubai-based airline began its wine program 12 years ago, it has spent more than $500 million to develop the best wine list in the sky... 'It’s an investment. We look at it like a commodity.'
- ^ Aydogdu, Hatice (November 15, 2005). "Oger Telecom signs $6.55 bln Turk Telekom deal". Reuters. Archived from the original on February 2, 2017. Retrieved January 30, 2017.
'... a long-term investment, not only in the future of Turk Telekom but also in Turkey,' Hariri said. The sale of Turk Telekom's controlling stake is a key element of Turkey's IMF-backed privatization program.
- ^ Thomas, Landon, Jr. (July 9, 2008). "Abu Dhabi buys 75% of Chrysler Building in latest trophy purchase". The New York Times. Retrieved December 29, 2016.
These funds, which maintain passive investment positions, will perform a crucial petrodollar-recycling function.
- ^ Bagli, Charles V. (July 10, 2008). "Abu Dhabi Buys 90% Stake in Chrysler Building". The New York Times. Retrieved July 3, 2016.
- ^ Lynch, Colum (December 11, 2009). "U.N. panel voices concern over Iran's apparent violations of arms-export embargo". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 29, 2017.
A U.N. sanctions committee expressed 'grave concern' Thursday about what it called apparent Iranian violations of a U.N. ban on arms exports.
- ^ Harel, Amos; Stern, Yoav (August 4, 2006). "Iranian Official Admits Tehran Supplied Missiles to Hezbollah". Haaretz. Retrieved March 29, 2017.
Mohtashami Pur, a one-time ambassador to Lebanon who currently holds the title of secretary-general of the 'Intifada conference', told an Iranian newspaper that Iran transferred the missiles to the Shi'ite militia.
- ^ Peers, Alexandra (February 2012). "Qatar Purchases Cézanne's The Card Players for More Than $250 Million, Highest Price Ever for a Work of Art". Vanity Fair. Retrieved February 19, 2016.
The money is there: the United Arab Emirates region is home to nearly 10 percent of all the world's oil reserve.
- ^ Business Monitor International (March 2016). "Q2 2016". Kuwait Autos Report. Retrieved January 13, 2017.
In 2015, Japanese carmaker Toyota retained its long-held local market leadership..., over three times its nearest rival Nissan.
Further reading
- Clark, William R. (2005). Petrodollar Warfare. New Society Publishers. ISBN 978-0-86571-514-1.
- Smolyar, Leonid (2006). Petrodollars: Tracking the Flow and Investment of Oil Windfalls (PDF) (B.Sc. Honors thesis). New York University. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 25, 2012.
- Staats, Elmer B. (1979). "The U.S.–Saudi Arabian Joint Commission on Economic Cooperation". U.S. Government Accountability Office. Retrieved January 31, 2016.